In this insight, we propose a pair trade between a basket of major securities stocks (long) versus banking stocks (short) in Korea.
We believe the five major securities stocks in Korea could continue to outperform the five major banking stocks in Korea over the next 6-12 months.
We present 3 major headwinds on the Korean banking sector and 4 major tailwinds on the Korean securities sector.
The five major Korean banking stocks include KB Financial (105560 KS), Shinhan Financial (055550 KS), Woori Financial Group (316140 KS), Hana Financial (086790 KS), and Industrial Bank Of Korea (024110 KS) [short a basket of these five stocks].
The five major Korean securities related stocks include Mirae Asset Securities (006800 KS), Meritz Financial Group (138040 KS), Korea Investment Holdings Co, Ltd. (071050 KS), Samsung Securities (016360 KS), and Nh Investment & Securities (005940 KS) [long a basket of these five stocks].
Three Major Headwinds on the Korean Banking Sector
The following are the three major headwinds on the Korean banking sector that could add to their weakness relative to the local securities firms:
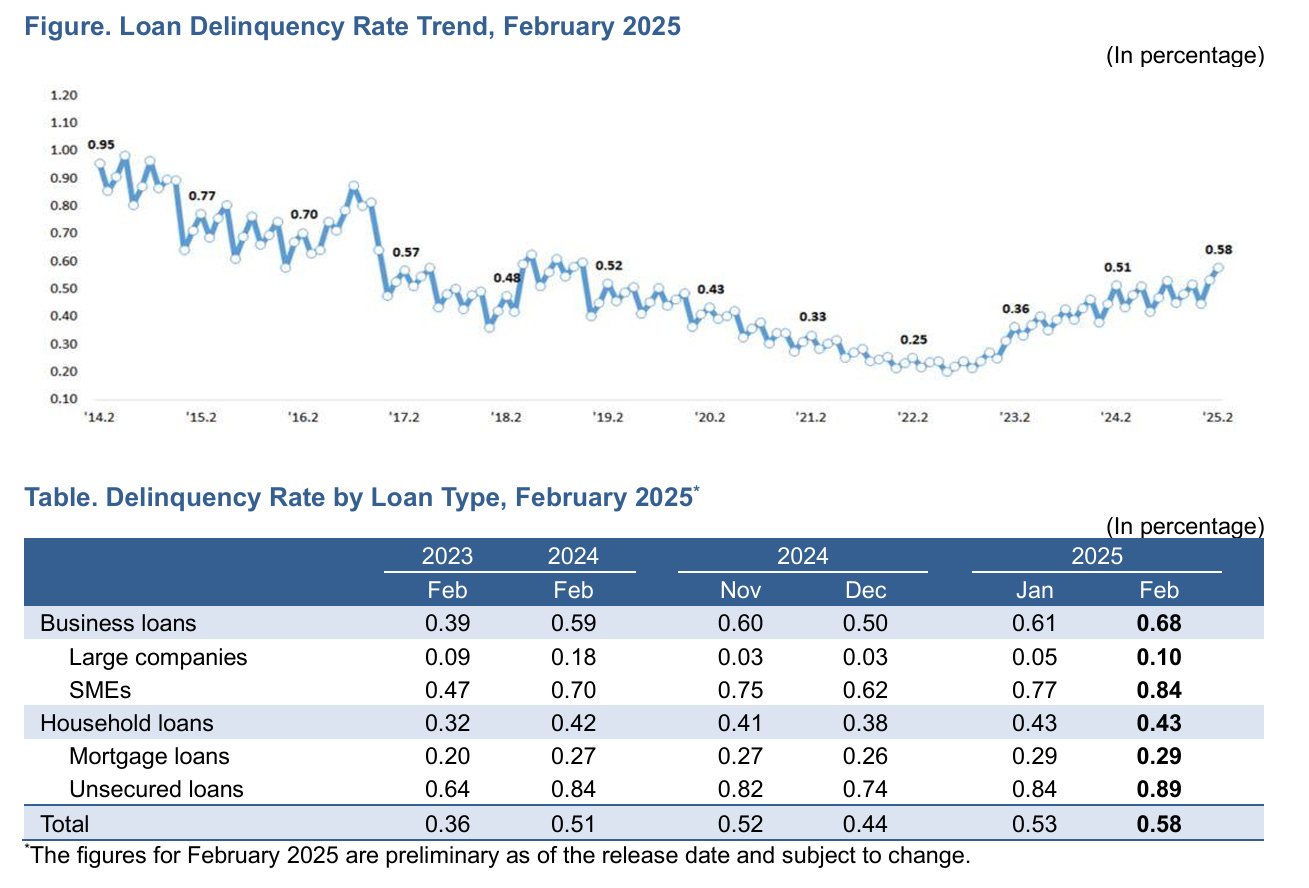
1) Continued Increase in Loan Delinquency Rates of Banks - The continued increase in the loan delinquency rates of Korean banks remains a big concern. The delinquency rate of domestic banks’ won-denominated (WD) loans was 0.58% as of end February 2025, up 0.05%p from a month earlier and up 0.07%p from a year earlier. The rate on loans to SMEs increased from 0.77% in January to 0.84% in February 2025. The delinquency on loans to SMEs in February 2025 is nearly double the rate in February 2023.
The loan delinquency rate of 0.58% in February 2025 was last reached in about six years and three years ago. Clearly, the rising loan delinquency rates since the lows in 2022 is a concerning trend.
There have been increasing news flow regarding continued weakness in the real estate sector in Korea (excluding some locations in Seoul and Sejong City) in the past 3 months. The weak real estate sector has put additional strains on thousands of SMEs and other businesses in Korea.
The loan delinquency rates of the major banks in Korea remain at less than 1%. However, the delinquency rates at major credit unions in Korea has been soaring. The delinquency rate of major credit unions in Korea increased from 3.63% in 2023 to 6.02% last year.
The delinquency rate of Saemaul Geumgo was 6.81 percent in 2024, up 1.74% points from 2023. The deep distress of the major credit unions such as Saemaul Geumgo is a canary in the coalmine. The deep financial distress of these credit unions could signal much weaker results at major banks in Korea, especially if the economy becomes worse.
Source: fss.or.kr
2) Lee Jae-Myung is the Leading Candidate for Next President (Increasing socialist policies that could lower profit margins of banks) - Lee Jae-Myung continues to lead in the Presidential polls (although the gap between Kim Moon-Soo has narrowed significantly in the past two weeks). As part of his policies, Lee Jae-Myung has pledged various policies including "basic loan" of 10 million won per citizen, and higher potential support for SMEs and public policies that could result in meaningful decline in profit margins of the Korean banks. For further detail, see our recent insight Lee Jae-Myung's Policies Likely to Negatively Impact Korean Banks.
3) Continued Decline in Korea's 10 Year Treasury Yield - South Korea's 10 year government bond yield has declined from its recent peak levels of 4.5% in October 2022 to 2.7% as of 15 May 2025. The decline in the treasury yield has made it more difficult for the major Korean banks to maintain their high NIM margins.
South Korea 10 year government bond yield (Source: South Korea 10 Years Bond - Historical Data)
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Douglas Research Insights to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.